
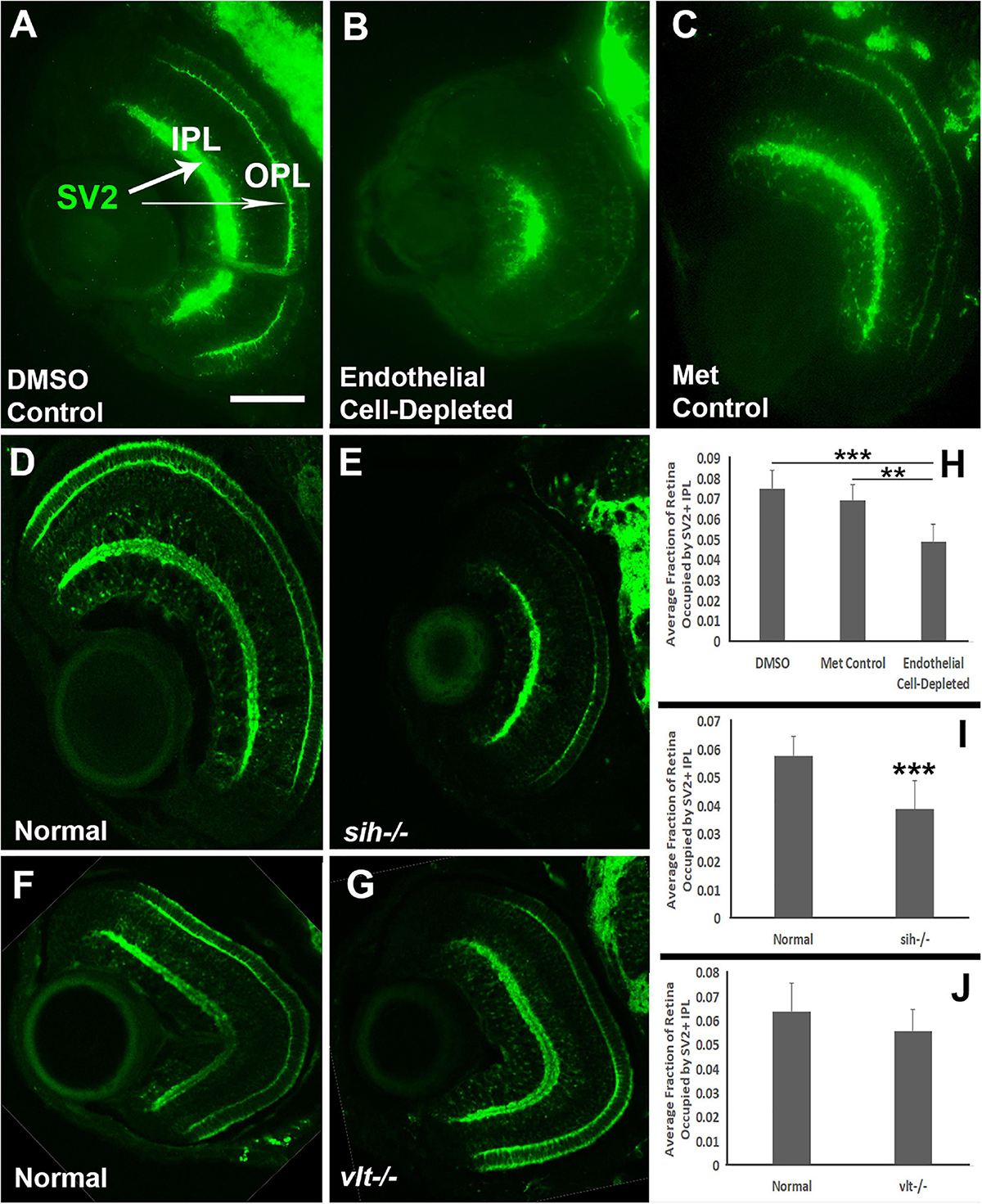
In this study, We derived the SVD/DVD ratio and identified factors that affect it. Therefore, we hypothesized that the factors affecting the normal retinal microvasculature would differ between the SCP and DCP. As such, the SCP and DCP can be differently affected by various conditions. reported a greater decrease in macular perfusion density of SCP than that of DCP in patients with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Another study found that VD of the DCP (DVD) decreased in abnormal multifocal electroretinography patients using hydroxychloroquine for rheumatoid arthritis, but VD in the SCP (SVD) did not. reported that changes in the fractal dimension in the DCP could be an early indicator of microvasculature changes associated with diabetic retinopathy. Previous studies have reported impairment of retinal microvasculature in various ophthalmic diseases using OCTA. OCTA yields various quantitative parameters including vessel density (VD), vessel length density, and the area of the foveal avascular zone (FAZ) of the superficial capillary plexus (from the internal limiting membrane to the inner plexiform layer SCP) and the deep capillary plexus (from the outer border of the IPL to the outer border of the outer plexiform layer DCP) with relatively high reliability. One of the advantages of OCTA is that the retinal microvasculature can be examined in each retinal layer and can be quantified. After the development of optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA), which is non-invasive and enables visualization of retinal microvasculature with high resolution, OCTA has replaced FA in many clinical fields. However, FA is invasive and time-consuming, and it is difficult to observe the retinal microvasculature in detail because of dye diffusion. Age, the BCVA, and OCTA quality were more strongly correlated with the SCP, and the axial length was more strongly correlated with the DCP.įluorescein angiography (FA) has been the gold standard for evaluation of the retinal microcirculation and microvasculature. ConclusionsĪge, BCVA, axial length, and OCTA image quality were significantly correlated with the SVD/DVD ratio. Pearson correlation analyses were performed to identify the relationships between this ratio and other factors. The ratio between the VD of SCP and DCP (SVD/DVD ratio) was calculated.
To identify factors differently affecting the superficial capillary plexus (SCP) and deep capillary plexus (DCP) in healthy eyes using their vessel density (VD) ratio.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
